In today's plumbing landscape, the significance of a water pressure reducing valve cannot be overstated. As per recent industry reports, approximately 85% of households experience issues related to high water pressure, leading to increased wear and tear on plumbing systems, inefficient water use, and even potential damage to appliances. The installation of an appropriate water pressure reducing valve can mitigate these risks, ensure optimal water flow, and enhance overall system efficiency. Moreover, statistics indicate that effective valve selection can result in a 30% reduction in water consumption, translating into significant cost savings over time. This ultimate guide aims to provide you with essential insights and tips for selecting the right water pressure reducing valve that meets your specific needs, ensuring that you not only protect your plumbing infrastructure but also promote sustainable water usage.
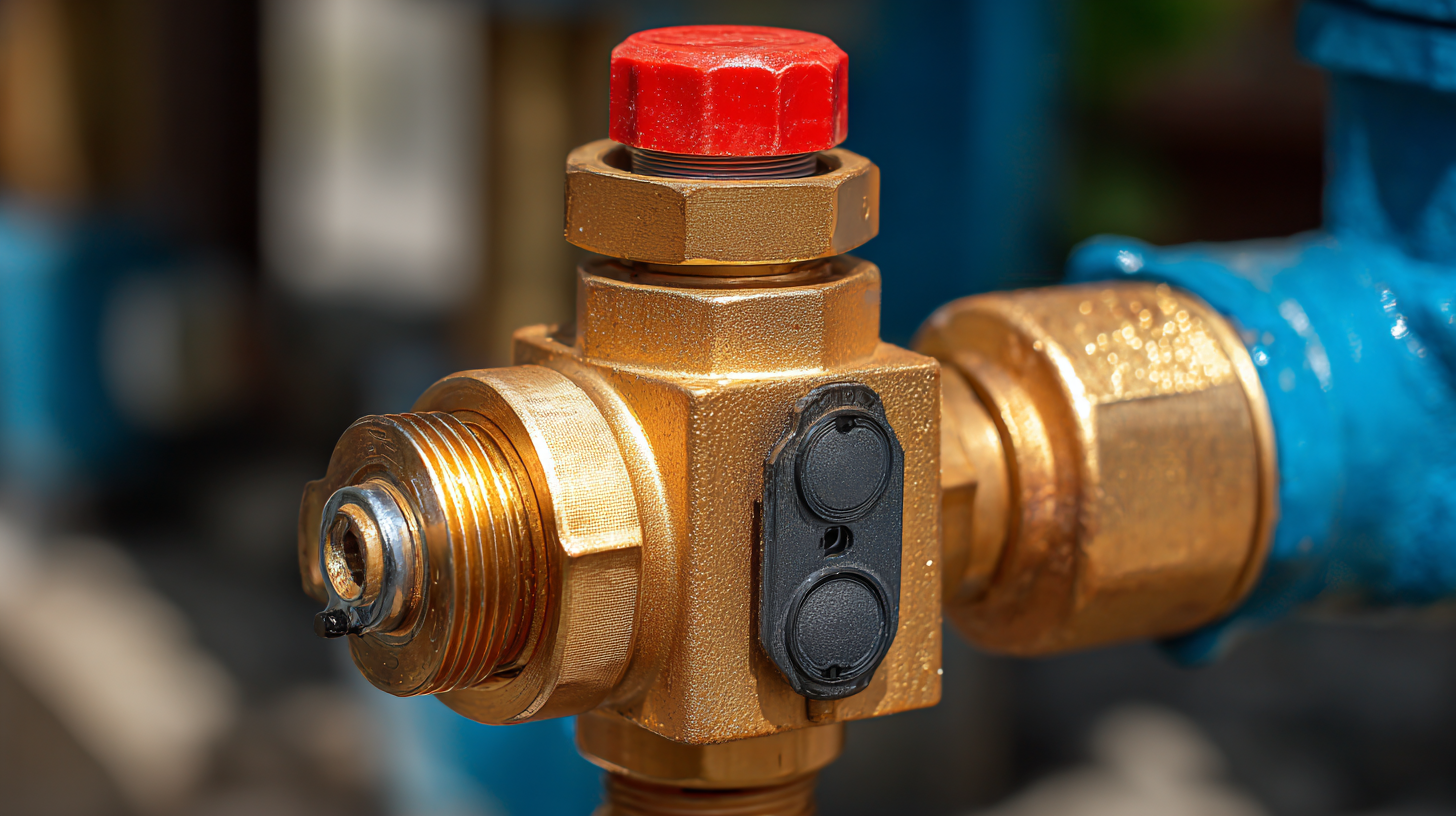
Water pressure reducing valves (PRVs) are essential components in modern plumbing systems, serving to maintain safe water pressure levels while protecting pipes and fixtures from damage. According to the American Society of Plumbing Engineers (ASPE), excessive water pressure can lead to leaks, burst pipes, and increased wear on appliances, emphasizing the critical role of PRVs in residential and commercial plumbing. By regulating incoming pressure, typically to a range of 40 to 60 psi, these valves ensure that water is delivered at an optimal force, enhancing both efficiency and longevity of plumbing systems.
Furthermore, data from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) highlights that well-regulated water pressure can contribute to energy savings, as it allows water-using appliances, such as washing machines and dishwashers, to operate more effectively. By minimizing pressure fluctuations, PRVs help reduce energy consumption by up to 10%, making them not only a protective measure but also a sustainable choice for homeowners seeking to lower utility costs. Investing in the right PRV therefore not only safeguards infrastructure but also aligns with energy-efficient practices, showcasing their importance in contemporary plumbing discussions.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Function | Reduces incoming water pressure to safe levels |
| Typical Pressure Range | 40 - 80 psi |
| Common Sizes | 1/2", 3/4", 1" |
| Materials | Bronze, plastic, stainless steel |
| Adjustability | Manual and automatic options available |
| Installation Location | Before the main water line enters the house |
| Maintenance | Regular checks for leaks and adjustments |
| Benefits | Protects plumbing fixtures, improves system longevity, lowers noise |
When selecting a water pressure reducing valve (PRV), understanding the various types available and their unique features is crucial to ensuring optimal performance and efficiency. There are primarily three categories of PRVs: direct-acting, pilot-operated, and bellows. Direct-acting valves are most commonly used in residential applications, effectively adjusting high inlet pressure to a safe, manageable outlet pressure with minimal complexity. According to the American Society of Plumbing Engineers, approximately 70% of residential plumbing systems utilize direct-acting PRVs due to their reliability and ease of installation.
Pilot-operated valves, on the other hand, are ideal for commercial and industrial use, where larger flow rates and pressure variations are present. These valves utilize a pilot system to sense downstream pressure, allowing for precise adjustments. A 2022 report by the Hydraulic Institute indicated that pilot-operated PRVs are capable of maintaining pressure within 1% of the set point, making them an excellent choice for applications requiring strict pressure control. Lastly, bellows valves, known for their ability to provide constant pressure even under fluctuating flow conditions, are perfect for sensitive systems such as irrigation and boiler systems. By understanding these distinct types, users can make informed decisions that meet their specific needs.
When selecting a water pressure reducing valve (PRV) for your home, several critical factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity. First, understanding the incoming water pressure is essential; according to the Plumbing Manufacturers International (PMI), residential water pressure typically ranges from 40 to 80 psi. However, excessive pressure can lead to leaks and damage. A reliable PRV should be capable of adjusting this pressure to a safe level, ideally between 50 to 60 psi, ensuring both appliance longevity and comfort.

Additionally, the size and flow rate of the PRV are vital to match the demands of your household. The American Society of Plumbing Engineers (ASPE) emphasizes that selecting a valve that can handle peak flow rates without causing excessive pressure drop is crucial. For instance, a valve rated at 10 gallons per minute (GPM) may suffice for smaller homes, but a larger household may require options rated for higher capacities to avoid performance issues during peak usage. Thus, carefully assessing these factors will lead to an informed decision, minimizing future plumbing complications.
 Installing a water pressure reducing valve (PRV) can significantly improve your plumbing system's performance, but ensuring its optimal functionality requires careful consideration during installation. Start by selecting a suitable location for the valve—typically, it should be positioned close to the main water supply line to effectively manage pressure levels before they reach your fixtures. Ensure that the surrounding space is accessible for future maintenance or adjustments, as PRVs may require occasional servicing to function correctly.
Installing a water pressure reducing valve (PRV) can significantly improve your plumbing system's performance, but ensuring its optimal functionality requires careful consideration during installation. Start by selecting a suitable location for the valve—typically, it should be positioned close to the main water supply line to effectively manage pressure levels before they reach your fixtures. Ensure that the surrounding space is accessible for future maintenance or adjustments, as PRVs may require occasional servicing to function correctly.
Once you’ve chosen the ideal spot, it’s crucial to prepare the existing plumbing. Turn off the water supply and drain the lines to avoid any messy surprises. Pay attention to the flow direction indicated on the valve; installing it backward can lead to inefficiency and pressure issues. Use Teflon tape on threaded connections to prevent leaks and secure each fitting tightly. After the installation, gradually restore the water supply while monitoring the valve's performance. Adjust the pressure settings according to your household needs, typically ranging between 40 to 60 psi, ensuring that your system operates smoothly and efficiently. Regular checks will help you maintain optimal performance and prolong the lifespan of your valve.
When selecting a water pressure reducing valve (PRV), one of the most common mistakes is not considering the pressure requirements of the system. According to the National Plumbing Foundation, improper pressure settings can lead to significant issues, including pipe leaks, increased wear on appliances, and reduced water efficiency. It is crucial to assess the incoming water pressure and match it with the desired pressure for the fixtures to ensure optimal performance and longevity of your plumbing system.
Another frequent error is neglecting to account for flow rates. A study conducted by the American Society of Plumbing Engineers highlights that selecting a PRV without understanding the specific flow needs of your household can result in inadequate pressure delivery during peak usage times. Miscalculating these factors can not only affect water delivery but may also lead to excessive energy costs as systems work harder to compensate for pressure loss. Always refer to detailed specifications and guidelines provided by manufacturers to avoid the pitfalls associated with oversizing or undersizing your valve.