In the realm of modern automation systems, the significance of pneumatic valves cannot be overstated. As industries increasingly adopt automation technologies, the market for pneumatic valves is projected to reach $20 billion by 2026, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 6.2% from 2021.
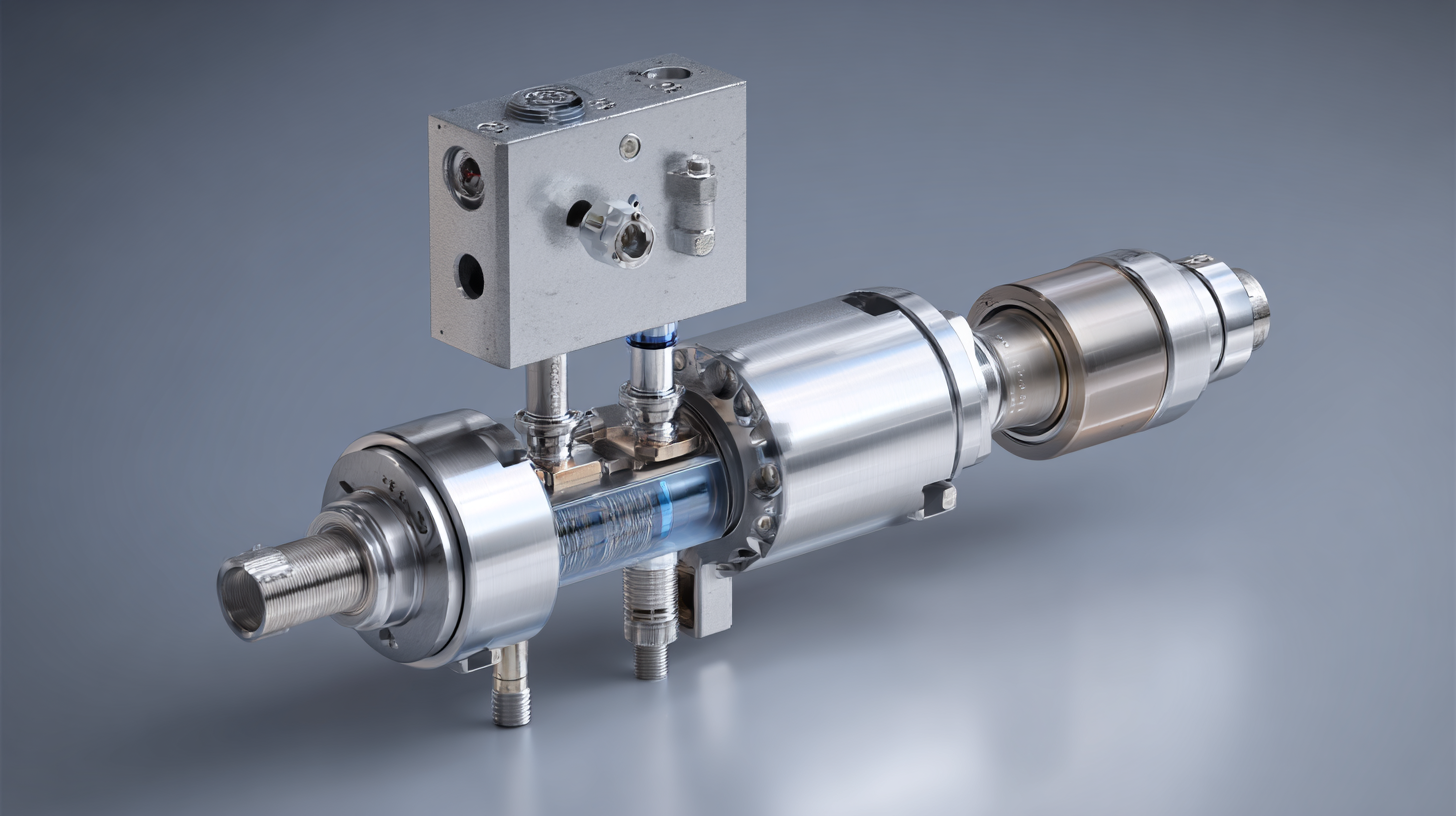 Pneumatic valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow and pressure of compressed air, thereby ensuring efficient operation and safety in various applications ranging from manufacturing to robotics. According to a study by MarketsandMarkets, advancements in valve design and the integration of smart technologies are reshaping the landscape, providing industries with enhanced reliability and performance. Understanding how to effectively implement pneumatic valves is essential for engineers and technicians looking to optimize automation processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Pneumatic valves play a crucial role in controlling the flow and pressure of compressed air, thereby ensuring efficient operation and safety in various applications ranging from manufacturing to robotics. According to a study by MarketsandMarkets, advancements in valve design and the integration of smart technologies are reshaping the landscape, providing industries with enhanced reliability and performance. Understanding how to effectively implement pneumatic valves is essential for engineers and technicians looking to optimize automation processes and improve overall operational efficiency.
Pneumatic valves play a critical role in modern automation frameworks, serving as essential components in various industrial processes. These valves control the flow and pressure of pneumatic systems, which are increasingly used in manufacturing and other sectors due to their flexibility and efficiency. Recent advancements highlight the integration of sophisticated control systems, such as the fractional-order proportional-integral-derivative (FOPID) controller, which enhances the performance of pneumatic control valves. This innovative controller is designed to minimize overshoot and provide rapid response, thereby improving the overall robustness of automation systems.
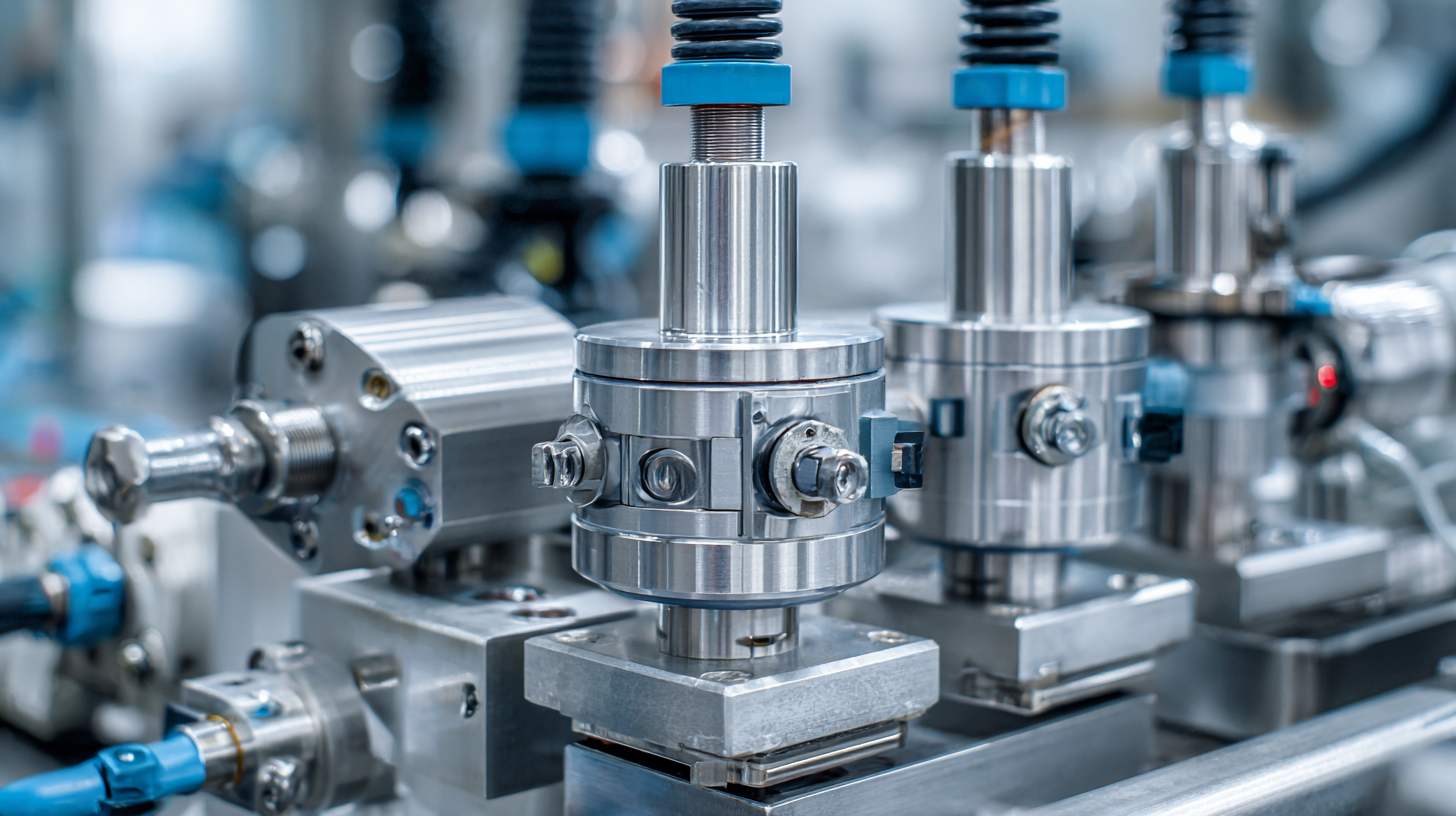

The ISA-96 series of standards is pivotal in guiding the specification, design, operation, and testing of valve actuators within these frameworks. By adhering to these standards, industries can ensure that their pneumatic valves meet required performance and safety benchmarks, contributing to more reliable automation processes. Research indicates that optimizing control algorithms for pneumatic systems can lead to significant gains in efficiency and stability, enhancing the competitiveness of enterprises that adopt these modern technologies.
Data shows that industries implementing advanced pneumatic controls can achieve response times 30% faster than traditional systems, demonstrating the potential for considerable operational improvements.
Pneumatic valves play a crucial role in modern automation systems, providing precise control over the movement of gases in industrial applications. There are several types of pneumatic valves, each designed to handle specific functions and requirements. Among the most common types are solenoid valves, which utilize electromagnetic coils to operate the valve, allowing for rapid switching and efficient control. These valves are widely used in automation systems where quick responses are essential, such as in assembly lines and packaging machinery.
Another important type is the directional control valve, which directs air flow to different parts of a system. These valves can be either manual or actuated by pneumatic means, enabling complex movements in machinery like robotic arms and conveyor systems. Additionally, pressure relief valves are essential for safety, regulating pressure within a system to prevent damage from pressure surges. Understanding the variety and application of pneumatic valves is key for optimizing automation processes, enhancing productivity, and ensuring safety in various industrial settings.
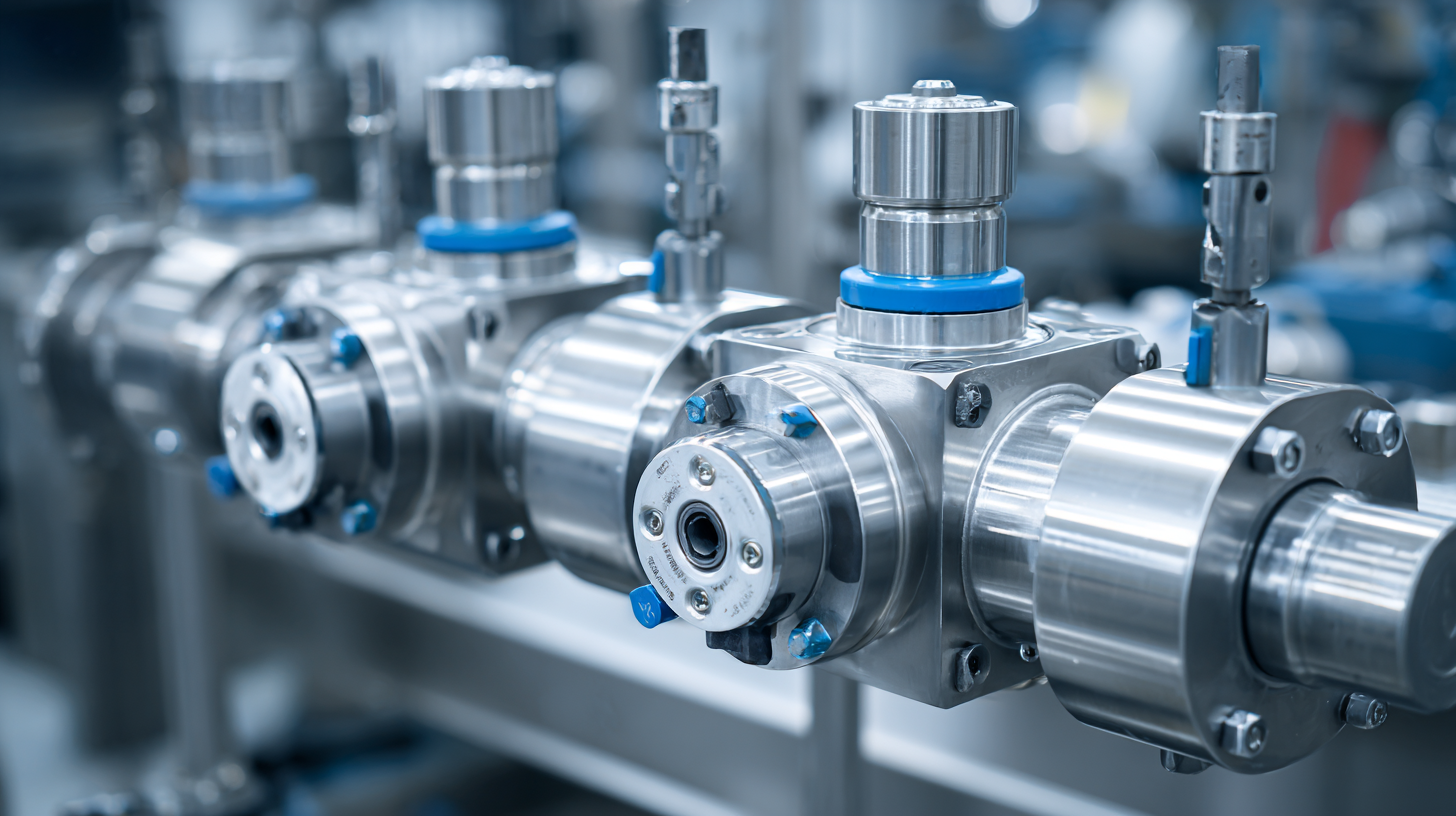

Pneumatic valves play a crucial role in the efficiency and reliability of modern automation systems. By controlling the flow of compressed air, these valves enable precise operation of machinery in various industrial applications. One of the primary benefits of integrating pneumatic valves into automated systems is their ability to enhance responsiveness. With rapid actuation times, these valves can react quickly to system demands, ensuring that processes are completed swiftly and accurately.
Another significant advantage of using pneumatic valves is their cost-effectiveness. Compared to electrical alternatives, pneumatic systems often require less initial investment and lower maintenance costs. Additionally, pneumatic valves can operate in harsh environments where electrical components might fail, making them ideal for demanding industrial applications. Their durability and simplicity contribute to reduced downtime, ultimately leading to increased productivity and efficiency in automated systems.
Pneumatic valves play a crucial role in modern automation systems by regulating the flow and pressure of air in various applications. However, like any mechanical component, these valves require regular maintenance and troubleshooting to ensure optimal performance. Effective maintenance practices can significantly reduce downtime and enhance the longevity of pneumatic systems.
One essential tip for maintaining pneumatic valves is to perform routine inspections. Check for signs of wear, leaks, or corrosion, which can cause valve malfunctions. Additionally, ensure that all connections are secure and that the operating pressure is within the manufacturer's specifications. Keeping your system clean and free of contaminants can also prevent issues from arising.
When troubleshooting pneumatic valves, it's vital to adopt a systematic approach. Begin by identifying any irregularities in the valve's operation, such as inconsistent airflow or longer-than-normal response times. Utilize diagnostic tools like pressure gauges and flow meters to pinpoint the source of the issue. Remember, addressing minor problems early on can prevent significant failures and costly repairs down the line. Always consult the manufacturer's guidelines for specific troubleshooting techniques tailored to your valve model.
This bar chart illustrates the maintenance and troubleshooting frequency of different types of pneumatic valves used in automation systems. The data showcases the importance of regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance and longevity of these components.
As the push for automation continues to reshape industries, pneumatic valve technology is evolving to meet demands for efficiency and reliability. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the global market for pneumatic valves is expected to reach $8.2 billion by 2025, driven by advancements in automation solutions across various sectors, including manufacturing, automotive, and food processing. These valves play a critical role in controlling airflow and pressure in pneumatic systems, directly influencing the performance and responsiveness of automated machinery.
Looking ahead, future trends are likely to center around digital integration and the Internet of Things (IoT). Pneumatic valves are becoming increasingly connected, allowing for real-time monitoring and data analytics to optimize performance. For instance, a study from Research and Markets indicates that integrating smart technologies with pneumatic systems can lead to a reduction in energy consumption by up to 30%, highlighting the potential for sustainability in automation. Furthermore, the development of more compact and robust valve designs is anticipated, which will enhance their functionality in constrained environments while maintaining high operational efficiency.
| Dimension | Current Trends | Future Innovations | Applications | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Increased focus on reducing energy consumption | Smart valves with adaptive energy usage capabilities | Manufacturing and packaging lines | High initial costs of smart technologies |
| Digital Connectivity | Integration with IoT devices | AI-powered predictive maintenance | Remote monitoring in various industries | Data security concerns |
| Automation Integration | Emphasis on fully automated systems | Seamless integration with robotics | Automated assembly lines | Compatibility with legacy systems |
| Material Innovation | Use of advanced composite materials | Biodegradable materials for sustainability | Environmental impact reduction | Material cost fluctuations |